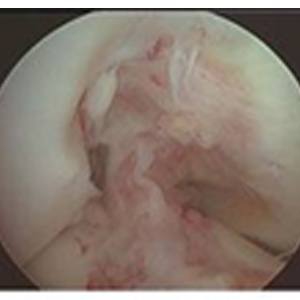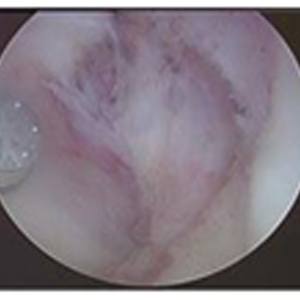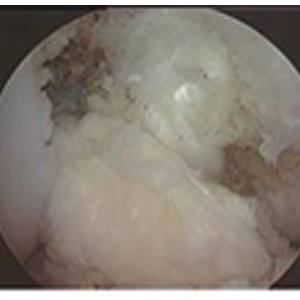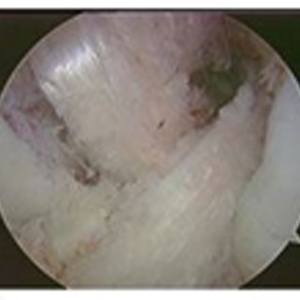
CAUSES
- Motorcycle injury
- Car Accident
- Rarely sports injury
PREOP
- X-ray
- MRI Scan-Evaluate all ligaments, meniscus, cartilage
- MRI Angiogram or other vascular study: ensure no vessel injury.
- CT scan: if fractured
TREATMENT OF MULTILIGAMENT KNEE INJURY
- Most multi-ligament knee injuries require surgery to restore stability to the knee.
- Once swelling is acceptable, all knee ligaments are repaired or reconstructed. Typically allograft tissue is used with or without internal bracing
RECOVERY
- Gentle range of motion and partial weight bearing is initiated between weeks 0-6 after incisions heal.
- The brace is removed at 6 weeks and full weight bearing is allowed.
- Near normal walking and range of motion is expected to return at 3-4 months after extensive physical therapy.
- Strengthening of the leg continues until months 9-12 when return to sports is usually allowed in a custom hinged knee brace.
- Multi-ligament knee injuries are very severe injuries. Despite a well-done surgery, range of motion deficit, strength deficit, limp, pain, knee instability, and limitation during sports can persist. Early arthritis in the knee can also develop.
DAY OF SURGERY
- General and block anesthesia
- Surgery can last 3-4 hours depending on the complexity of the injury.
- 1-2 night hospital stay
SUCCESS RATE
- 75% return to sport
- 20% reoperation rate
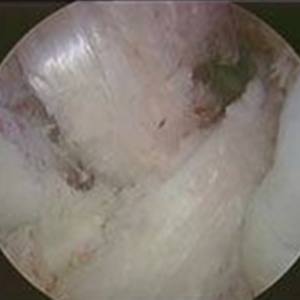
Before
After ACL/PCL Reconstruction
Questions?
Email Dr. Gamradt - [javascript protected email address]
[javascript protected email address] Office Phone: